Applications of chemical kinetics in unit process
This includes analysis of conditions that affect speed of a chemical reaction , understanding reaction mechanisms and transition states, and forming mathematical models to predict and describe a chemical reaction.
A Brief Introduction to the History of Chemical Kinetics
The field of chemical kinetics developed from the law of mass action, formulated in by Peter Waage and Cato Guldberg. The law of mass action states the speed of a chemical reaction is proportional to the amount of reactants. Jacobus van't Hoff studied chemical dynamics. His publication "Etudes de dynamique chimique" led to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry which was the first year the Nobel prize was awarded. Experimental data is used to find reaction rates, from which rate laws and chemical kinetics rate constants are derived by applying the law of mass action.
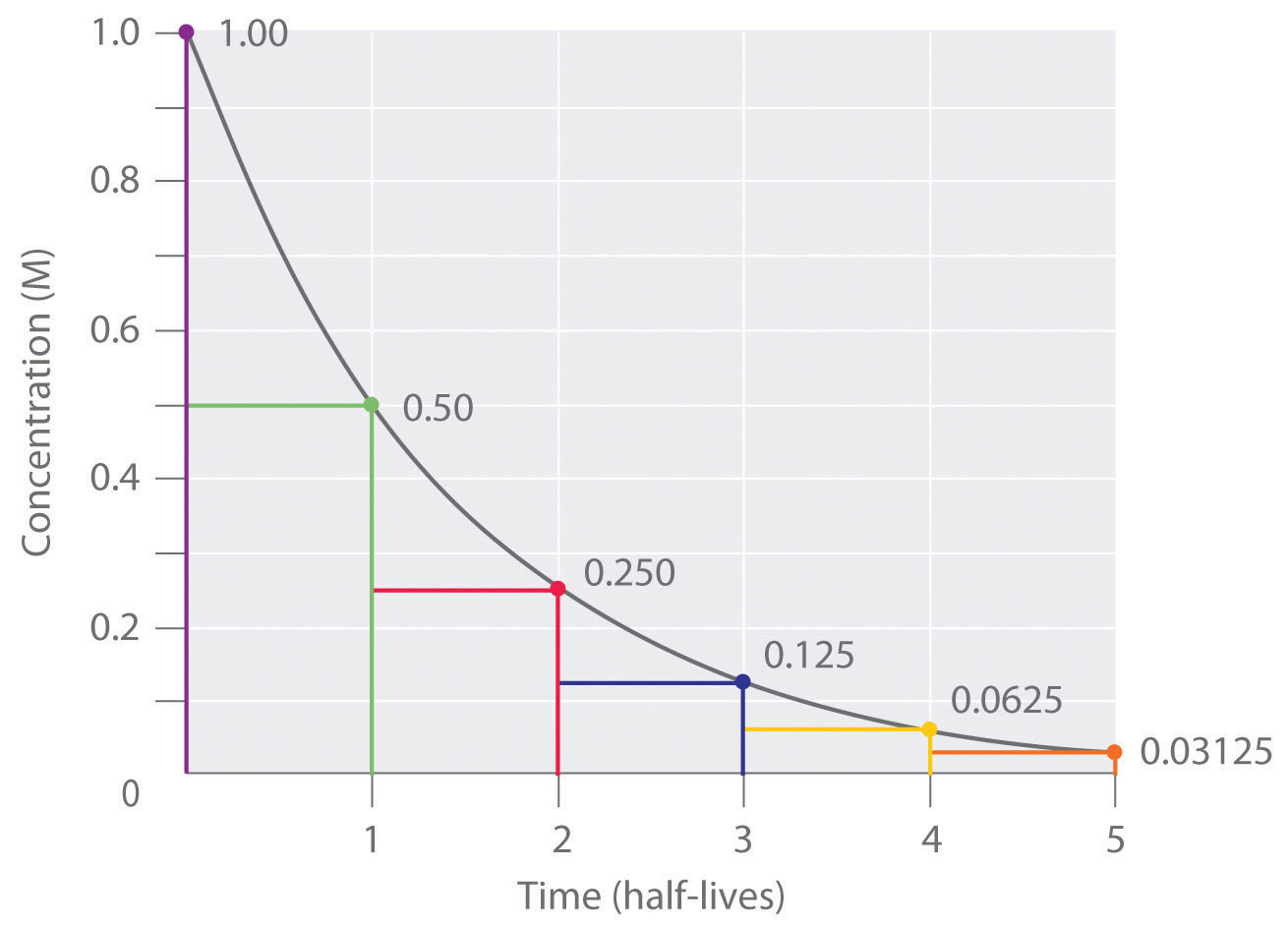
Rate laws allow for simple calculations for zero order reactions, first order reactions, and second order reactions. Rate laws for individual steps must be combined to derive laws for more complex chemical reactions. For these reactions:. Chemical kinetics predicts the rate of a chemical reaction will be increased by factors that increase the kinetic energy of the reactants up to a point , leading to increased likelihood the reactants will interact with each other. Similarly, factors that decrease the chance of reactants colliding with each other may be expected to lower the reaction rate.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
The main factors that affect reaction rate are:. Note that while chemical kinetics can predict the rate of a chemical reaction, it does not determine the extent to which the reaction occurs.
- Chemical kinetics!
- Chemical Kinetics Research Papers - phon-er.com.
- Hypothesis and Theory ARTICLE!
- Find out for yourself!
Thermodynamics is used to predict equilibrium. Some chemical reactions are neither slow nor fast but take place at a moderate rate. The speed or rate of a chemical reaction is the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time.
- king of fighter 97 nokia x2.
- samsung galaxy s4 active photo recovery.
- google chrome browser for nokia 5800 xpressmusic.
- Study-Unit Description?
- compact and author info!
- Publication details;
- 14.S: Chemical Kinetics (Summary)!
- applications of decoder in traffic light.
- Chemical kinetics.
To be specific, it can be expressed in terms of:. Consider a reaction in which the total volume of the system remains constant. Let R be the reactants and P be the products i.
Thus, one mole of reactant R produces one mole of product P. Let the initial concentration of R be [R] 1 and the concentration of P be [P] 1 at time t 1. Therefore at time t 2 , the concentrations of R and P are [R] 2 and [P] 2 respectively.
The above equations give the average rate of a chemical reaction which is, r av. Therefore, the average rate of a reaction depends upon the change in concentrations of the reactants or products and the time taken for that change to occur. It is clear from equations I and II that the unit of rate of a reaction is concentration time Solution: The average rate of a chemical reaction is the change in the concentration of the reactant or product divided by the time taken for that reaction to occur.
What Is Chemical Kinetics?
Solution : The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration of the reactant or product divided by the change in time. Therefore, the formula of rate of reaction for the above reaction would be:. Learning Outcomes: 1. Skills : By the end of the study-unit the student will be able to: - Carry out calculations which can predict reactivity under a set of conditions; - Work out rate laws for various reaction mechanisms; - Perform experiments in physical chemistry and collect data from them in safe and reliable manner; - Check the correctness and reliability of experimental results from physical chemistry experiments; - Interpret correctly and verify the results of experimental work related to physical chemistry; - Discuss results of experimental work in relation to established knowledge physical chemistry and chemistry in general; - Report the findings of an experiment in a scientific manner.
Atkins and Julio de Paula, 10th ed.
3 Campuses, 20 Institutes, Infinite prospects
Please note that a pass in the Practical component is obligatory for an overall pass mark to be awarded. The University makes every effort to ensure that the published Courses Plans, Programmes of Study and Study-Unit information are complete and up-to-date at the time of publication. The University reserves the right to make changes in case errors are detected after publication.