Applications astable multivibrator using 555 timer
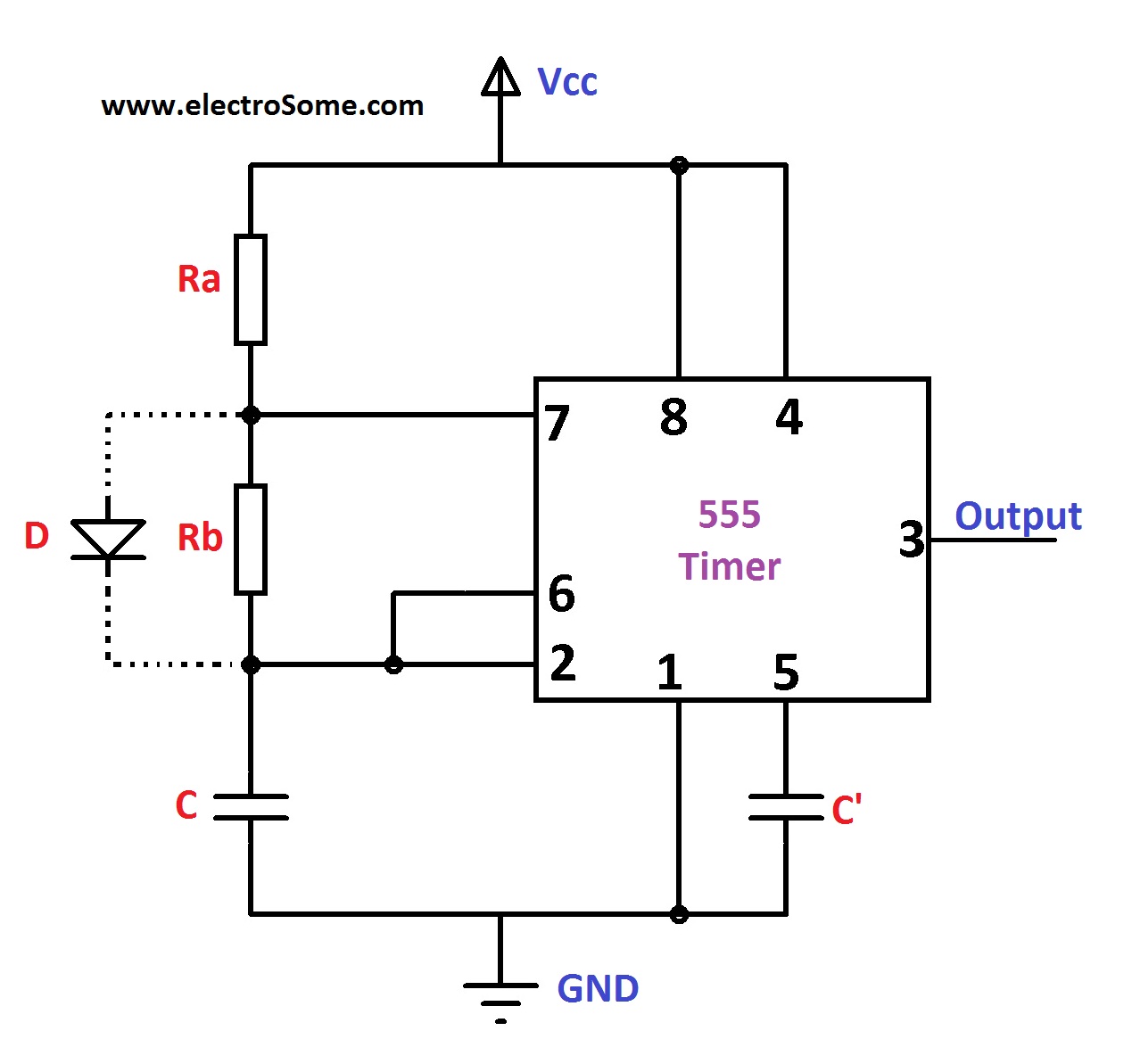
The circuits changes its state alternately. Hence the operation is also called free running nonsinusoidal oscillator. When the flip-flop is set, Q is high which drives the transistor Qd in saturation and the capacitor gets discharged. Now the capacitor voltage is nothing but the trigger voltage. This resets the flip-flop hence Q goes low and Q goes high. The low Q makes the transistor off. The charging path is shown by thick arrows in the Fig. Now the capacitor voltage is also a threshold voltage. While charging, capacitor voltage increases i.
The flip-flop output Q becomes high and output at pin 3 i. Q becomes low. High Q drives transistor Q d in saturation and capacitor starts discharging through resistance R 8 and transistor Q d. This path is shown by dotted arrows in the Fig. Thus the discharging time constant is R B C.
This cycle repeats. The output is a rectangular wave. The capacitor voltage is exponentially rising and falling.
- Astable Multivibrator Working;
- antenna gps bluetooth su ipad;
- Electronics For You!
- Demo of 555 timer-based astable multivibrator using MATLAB.
- ipad apps for long distance relationships!
The waveforms are shown in the Fig. Generally the charging time constant is greater than the discharging time constant. Hence at the output, the waveform is not symmetric. The high output remains for longer period than low output. The ratio of high output period and low output period is given by a mathematical parameter called duty cycle.
Astable Multivibrator Using 555 Timer
It is defined as the ratio of ON time i. As shown in the Fig. The pin 4 is tied to pin 8 and pin 5 is grounded through a small capacitor. The important application of astable multivibrator is voltage controlled oscillator VCO. Your email address will not be published. Search for: Basic Log Amplifier Using Diode. A multivibrator is a one type of electronic circuit , that is used to implement a two state system like flip-flops, timers and oscillators. Multivibrators are categorized by two amplifying devices like electron tubes, transistors and other devices like capacitors and cross coupled by resistors.
Multivibrators are classified into three types based on the circuit operation, namely Astable multivibrators, Bistable multivibrators and Monostable multivibrators. The astable multivibrator is not stable and it repeatedly switches from one state to the other. In monostable multivibrator, one state is stable and remaining state is unstable.
A trigger pulse is the root to the circuit to enter the unstable state. When the circuit enters into the unstable state, then it will return to the normal state after a fixed time.
User login
A bistable mutivibrator circuit is stable that can be changed from one stable to other stable by an external trigger pulse. This multivibrator circuit is also called as flip-flop which can be used to store one bit of data. This type of multivibrator includes two amplifying stages that are connected with a two capacitive-resistive coupling networks in a positive feedback.
The astable multivibrator circuit using BJTs is drawn in the form of cross coupled pair.
Astable Multivibrator Using IC I Operation I Applications
It is employed by the coupling capacitors that suddenly transfer voltage variations because the voltage across a capacitor cannot change quickly. In every state, one transistor is turned on and the remaining one is turned off. So, one fully charged capacitor discharges slowly, therefore changing the time into an exponentially altering voltage.
At the same time, remaining empty capacitor charges quickly. The operation of the above circuit is based on the forward-biased BE junction of the turned on BJT, that can provide a route for the restoration of the capacitor. The timer IC affords exact time delay from ms to hours. The oscillation frequency can be measured manually by small modification. The first integrated circuit was designed in the year by the corporation of Signetics as the SE or NE Astable multivibrator using IC is a simple oscillator circuit that generates continuous pulses.